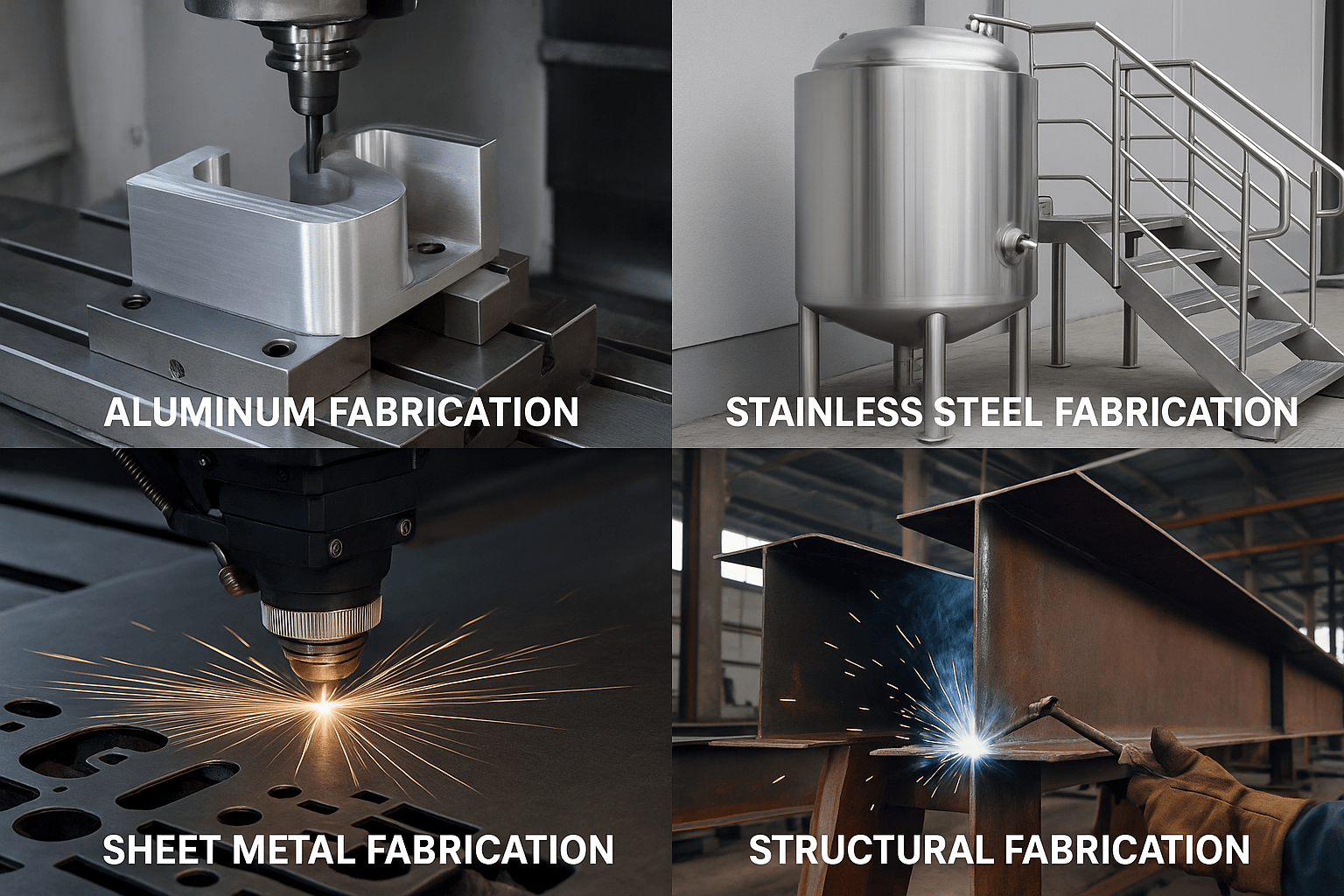
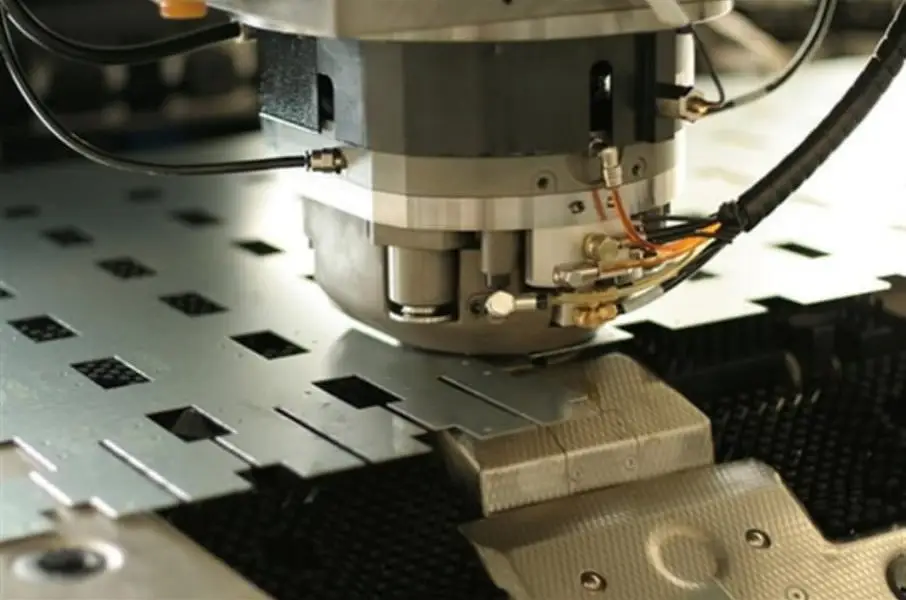
Global Sheet Metal Manufacturing | Engineering Excellence Delivered

Introduction
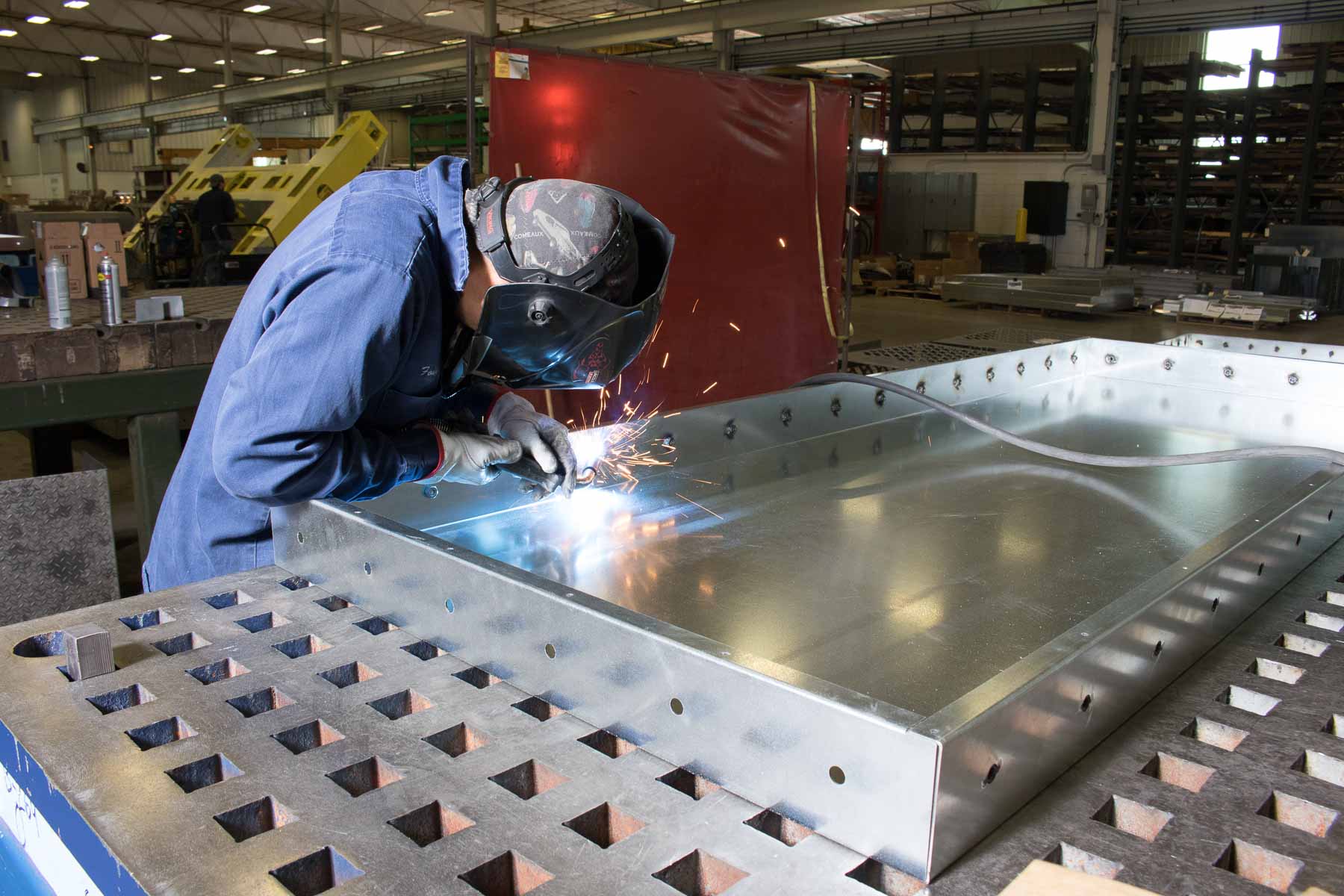
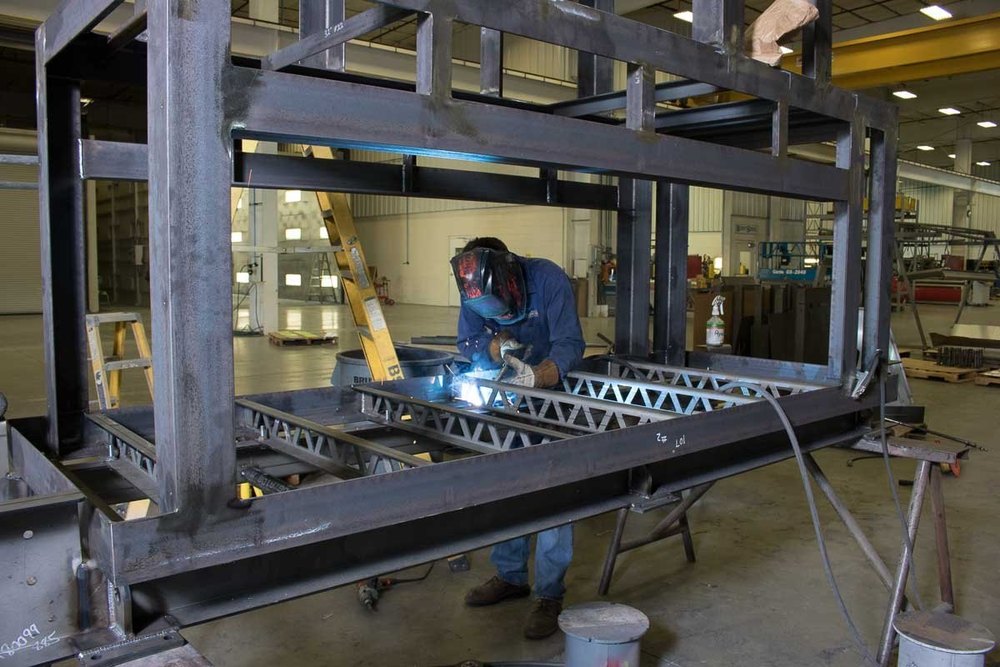
In today’s highly industrialized world, sheet metal manufacturing forms the backbone of countless industries. From aerospace components to consumer electronics, construction frameworks to automotive assemblies, sheet metal parts are everywhere. The process combines centuries-old metalworking practices with cutting-edge engineering, advanced automation, and digital innovation. As global demand continues to rise, sheet metal manufacturers must deliver not only high-quality products but also engineering excellence, operational efficiency, and sustainable solutions.
This blog explores the global sheet metal manufacturing landscape, highlighting industry growth, technologies, applications, challenges, and the engineering precision that drives excellence in this dynamic sector.

The Global Landscape of Sheet Metal Manufacturing
Sheet metal manufacturing has evolved from a localized, craft-based trade into a globalized industry with multi-billion-dollar value. According to industry estimates, the global sheet metal fabrication services market is projected to surpass USD 20 billion by 2030, driven by rising demand across construction, automotive, energy, and industrial sectors.
Key regions dominating the market include:
-
Asia-Pacific (APAC) – China, India, and Japan lead production with strong supply chains, cost advantages, and massive industrial bases.
-
North America – The U.S. and Canada focus on innovation, precision manufacturing, and aerospace/defense applications.
-
Europe – Germany, Italy, and the UK specialize in high-quality sheet metal solutions for automotive, medical devices, and industrial equipment.
This global distribution creates a competitive yet collaborative marketplace where companies leverage engineering expertise and advanced technologies to deliver excellence.
Engineering Excellence in Sheet Metal Manufacturing
Engineering excellence in sheet metal manufacturing is achieved through precision, efficiency, and innovation. Manufacturers today rely on an ecosystem of advanced design tools, high-tech machinery, and process optimization strategies. The key drivers of excellence include:
1. Precision Engineering and Tolerances
Every millimeter matters in sheet metal work. Whether it’s bending, cutting, or stamping, engineers ensure dimensional accuracy through CAD/CAM software and Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines. Tighter tolerances improve product performance and reduce material waste.
2. Automation and Robotics
Automation has transformed global sheet metal production lines. Robotic arms, laser cutters, and automated bending machines reduce human error, accelerate output, and enable mass customization.
3. Material Science Advancements
Modern sheet metal is no longer just steel and aluminum. High-strength alloys, corrosion-resistant coatings, and lightweight composites are engineered for specialized applications such as electric vehicles and aerospace.
4. Digital Manufacturing and Industry 4.0
The integration of IoT sensors, AI-driven monitoring, and digital twins ensures real-time tracking of production performance, predictive maintenance, and data-driven decision-making. This enhances efficiency while reducing downtime.

Applications Across Global Industries
Sheet metal’s versatility makes it indispensable in global manufacturing. Here are some of the key industries where it plays a vital role:
Automotive and Transportation
From chassis frames to body panels, exhaust systems to electric vehicle battery housings, sheet metal is fundamental to automotive design. Precision forming techniques deliver lightweight yet durable components that improve fuel efficiency and safety.
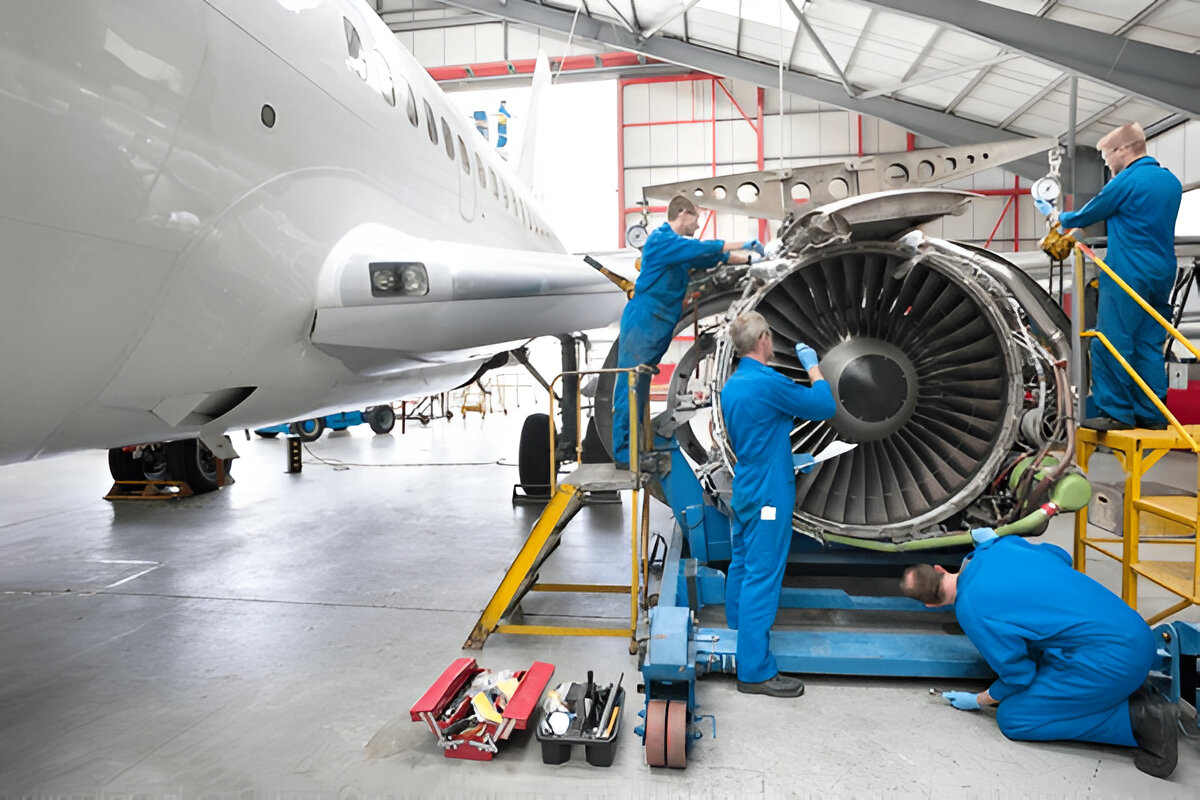
Aerospace and Defense
Aircraft rely on lightweight, high-strength sheet metal for fuselage structures, engine components, and interior fittings. The defense sector also uses sheet metal for armored vehicles, naval equipment, and weapon systems.
Construction and Infrastructure
Sheet metal is used in roofing, HVAC systems, cladding, and structural supports. Prefabricated sheet metal solutions reduce on-site labor, improve installation times, and deliver sustainability benefits.
Consumer Electronics and Appliances
Smartphones, laptops, and kitchen appliances depend on sheet metal enclosures for strength, thermal conductivity, and design aesthetics.
Renewable Energy and Power
Wind turbines, solar panel mounts, and energy storage systems incorporate sheet metal components designed for efficiency and durability under extreme conditions.
Challenges in Global Sheet Metal Manufacturing
Despite its growth and applications, the industry faces several challenges that test engineering excellence:
-
Supply Chain Volatility – Global fluctuations in raw material costs (steel, aluminum) impact profitability.
-
Skilled Labor Shortages – Advanced machinery requires skilled operators and engineers, which are in short supply worldwide.
-
Sustainability Pressure – With stricter environmental regulations, manufacturers must adopt greener production methods, reduce emissions, and improve recyclability.
-
Technological Integration – While automation is a boon, integrating AI, IoT, and robotics requires significant investment.
-
Global Competition – Manufacturers in high-cost economies must compete with low-cost production hubs while maintaining quality and innovation.
Innovations Driving the Future
The future of sheet metal manufacturing is being reshaped by innovations that deliver engineering excellence on a global scale:
-
Additive Manufacturing (Metal 3D Printing): Enables rapid prototyping, customization, and reduced material waste.
-
AI-Powered Design Optimization: Artificial intelligence analyzes designs to suggest improvements in strength, weight, and material usage.
-
Smart Factories: Connected manufacturing ecosystems integrate machines, sensors, and analytics for fully automated production.
-
Sustainable Manufacturing Practices: Use of renewable energy in production, water recycling, and eco-friendly coatings align with global green initiatives.
-
Collaborative Robotics (Cobots): Human-robot collaboration enhances productivity and safety in fabrication facilities.
Delivering Engineering Excellence Globally
Engineering excellence in sheet metal manufacturing is not limited to technology—it extends to every stage of the production cycle:
-
Design Excellence – Using CAD/CAM for precision and innovation in product development.
-
Production Excellence – Lean manufacturing principles ensure cost efficiency and waste reduction.
-
Quality Assurance – Global standards such as ISO 9001, AS9100, and IATF 16949 guide manufacturers toward consistent quality.
-
Supply Chain Excellence – Building resilient networks for uninterrupted material availability and timely delivery.
-
Customer-Centric Excellence – Providing tailored solutions that meet industry-specific needs, from prototyping to large-scale production.
By integrating these dimensions, manufacturers achieve a competitive advantage and establish trust with global customers.
Sustainability in Sheet Metal Manufacturing
In a world increasingly focused on environmental impact, sustainability is becoming central to engineering excellence. Manufacturers are:
-
Recycling Scrap Metals – Nearly 90% of sheet metal scrap can be recycled, reducing raw material dependence.
-
Energy-Efficient Processes – Using fiber laser cutting instead of traditional CO₂ lasers reduces power consumption.
-
Eco-Friendly Materials – Lightweight, recyclable metals reduce carbon footprints in automotive and construction industries.
-
Green Certifications – Meeting LEED and ISO 14001 standards ensures global compliance and improved brand reputation.
Sustainable practices not only protect the environment but also drive cost savings and long-term competitiveness.
The Human Element: Skilled Engineering Workforce
While machines and automation dominate headlines, the role of skilled engineers, designers, and technicians remains irreplaceable. Human expertise ensures:
-
Innovative product design.
-
Problem-solving in complex manufacturing challenges.
-
Continuous process improvement.
-
Safe operations and ethical practices.
Global training programs, apprenticeships, and collaborations with engineering universities are essential to prepare the next generation of sheet metal experts.
Conclusion

Global sheet metal manufacturing is more than just cutting and forming metal—it is the fusion of engineering excellence, innovation, and precision. From automobiles to aircraft, skyscrapers to smartphones, sheet metal components touch every aspect of modern life.
As the industry evolves, digital transformation, sustainability, and global collaboration will define its trajectory. Companies that deliver engineering excellence by embracing advanced technologies, maintaining quality, and prioritizing customer needs will continue to lead the way in this competitive market.
In essence, sheet metal manufacturing is not just about shaping metals—it’s about shaping the future of industries worldwide.