Different types of Metal Fabrication: Advanced Technologies, processes and Applications.
Different types of Metal Fabrication: Advanced Technologies, processes and Applications.
Metal Fabrication lies at the heart of industry, creating the tools we use, the vehicles we rely on, and the networks that connect us. Metal fabrication builds structures It’s the roof over our head, the car on our driveway, the grill up on our balcony. This to-the-point examination breaks down all the types of fabrication and highlights sheet metal fabrication, but also how structural fabrication, metal manufacturing, stainless steel fabrication, aluminum fabrication, and industrial fabrication have their own processes and uses.
Basics of Metal Fabrication

Metal fabrication is the building of metal structures by cutting, bending, and assembling processes which is a value added process that involves the construction of machines and structures from various raw materials. To make any kind of metal productive in production and construction, it is necessary to shape it with special forming methods, adapted to the respective purpose. These process not only form the metal, but also improve its properties, exemplifying its flexibility in various forms.
The manufacturing field has changed dramatically with the development of technology making available new tools and machines that allow for more accurate, efficient and complex manufacturing processes. The metal fabrication, runs its gamut and the raw materials are shaped into miscellaneous shapes and fabricated or monolithic items by means of fabricating processes, which can be classified, inter-alia, into cutting, forming, joining and finishing operations4.
Primary Metal Fabrication Processes
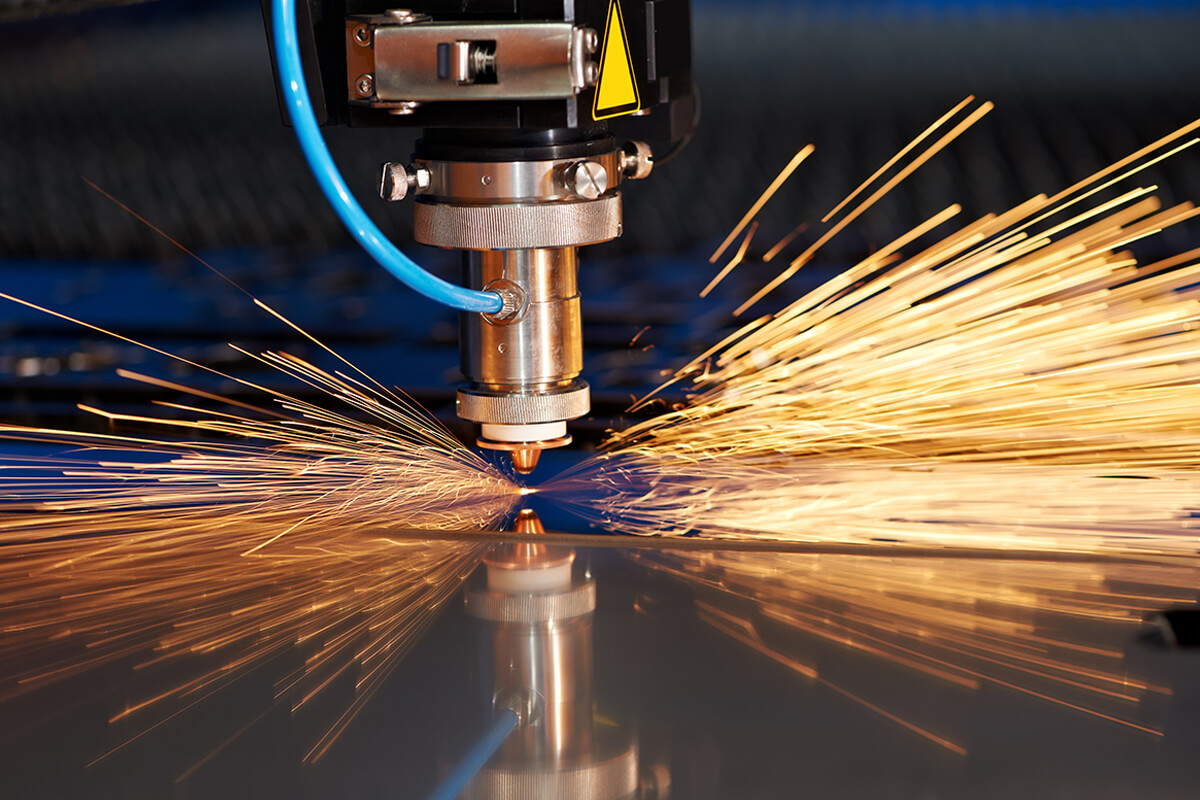
Cutting: The Initial Key Factor
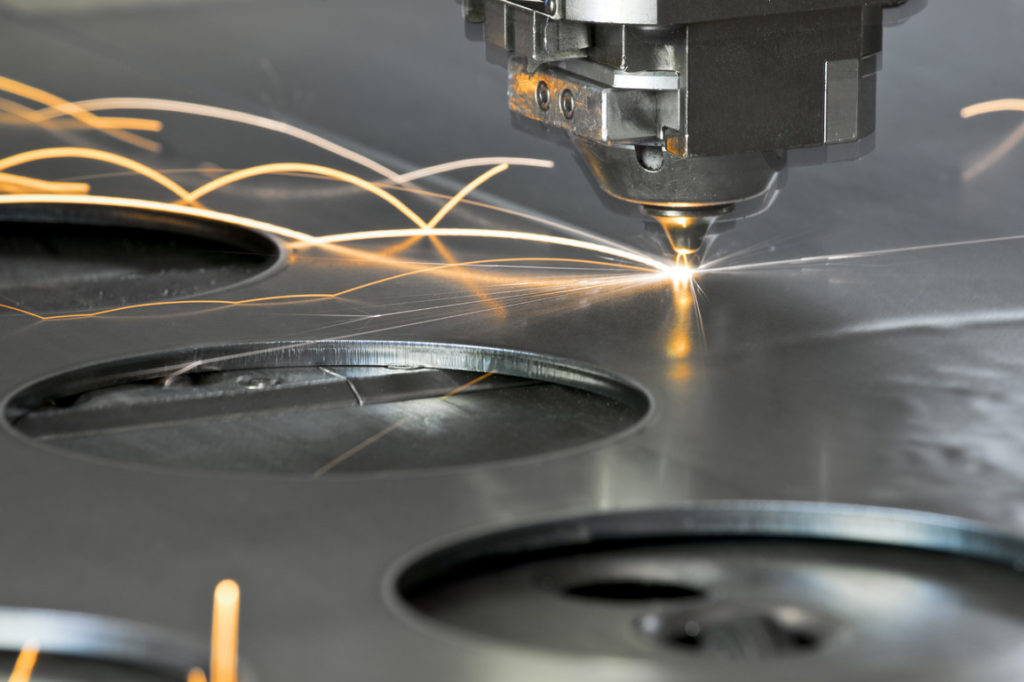
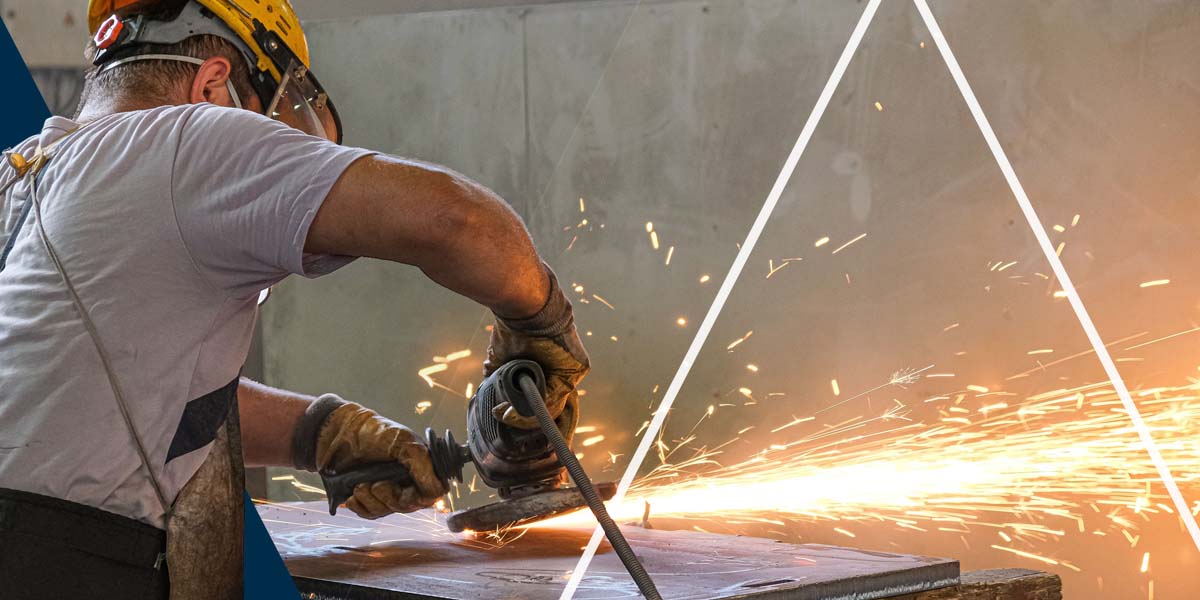
Cutting is one of the oldest and most fundamental of the metal fabrication processes . Such a process is the process of cutting of unnecessary material in the workpiece to obtain a workpiece of the desired shape and dimensions. Modern cutting technologies have advanced far beyond traditional methods, offering unprecedented precision and efficiency.
In modern day fabrication in India, the cutting process are likely to utilize various recent cutting technologies:
- Laser Cutting High-powered density laser to melt, vaporize, or eradicate material to cut very accurately. Laser cutting machines are very good for aluminum, steel, copper, and stainless steel, especially for thin materials (up to 20mm for aluminum and 32 mm for Mild steel / Carbon Steel/MS).
- Waterjet Cutting: Uses high-pressure jets of water, sometimes mixed with abrasive materials, to cut through metal with little heat distortion.
- Plasma Cutting: This is the process of cutting a material using a plasma torch, and is commonly used for cutting electrically conductive materials.
- Mechanical Cutting: Incorporates the conventional physical apparatus and equipment reliant sawing, shearing, or punching.
In the production process, cutting processes are in general the beginning of manufacturing chains to generate basic structures, which are then modified in machine tools. The choice of cutting method is based upon the type of material being cut, its thickness, the desired accuracy and the quantity to be produced.
Forming: Shaping Metal Through Deformation
After cutting, metal components often undergo forming operations that alter their shape without removing material:
Bending : Deforms metal along a straight axis, such operations used in sheet metal process to make lines, angles, channels and other forms. Bending is a metal forming process in which a force is applied to a piece of metal, causing it to bend at an angle and to form the desired shape (curls, pocket folds, hemming, and so on).
Stamping: Equipment that uses dies to shape or cut sheet metal in a press, excellent for producing large quantities of identical parts.
Extrusion: Drives metal through a die to produce shapes with a constant cross-section; typically used for tubing, pipes, and structural members.
Forging: The application of compressive forces to metal, usually with high-pressure equipment, reshaping and strengthening it, creating parts which have superior stiffness characteristics.
Casting: It is referred to as pouring liquid metal into a mold which constitutes the die and the liquid solidifies as it cools, assuming the shape of the die.
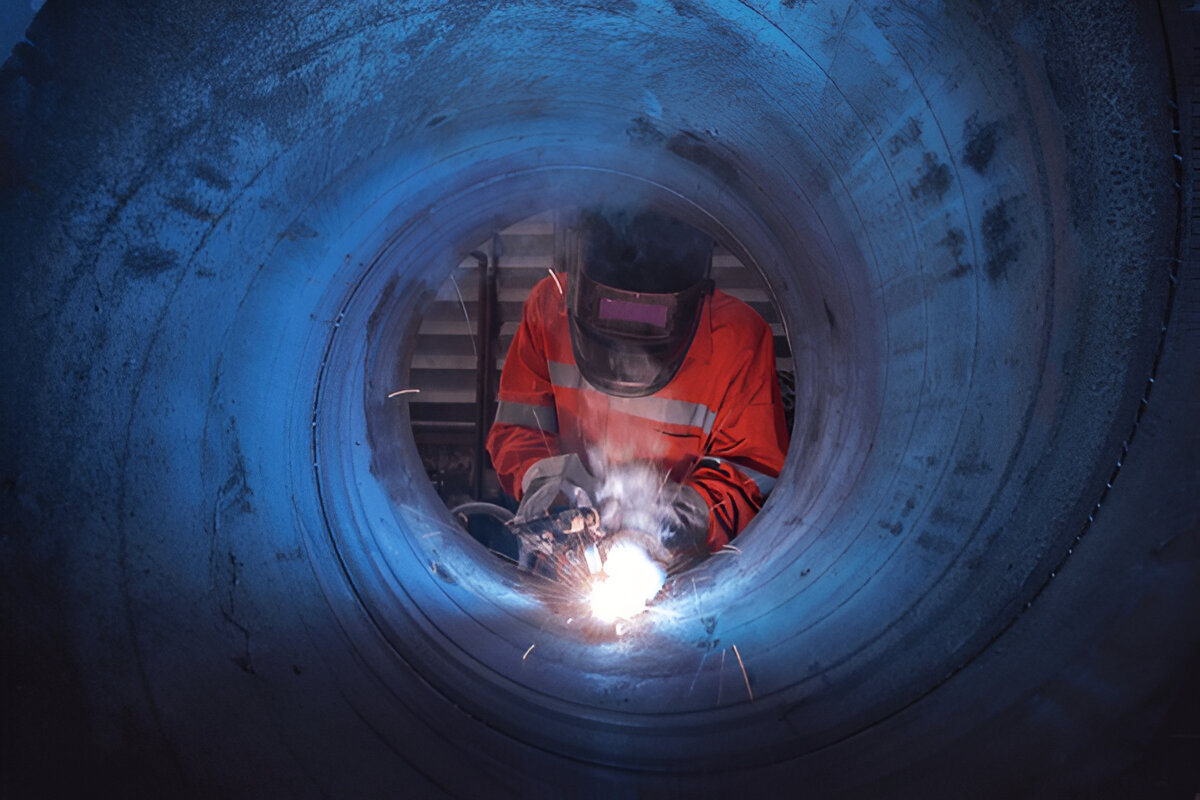
Joining: Creating Complex Assemblies
Joining operations join different metal components to obtain more complex Structures:
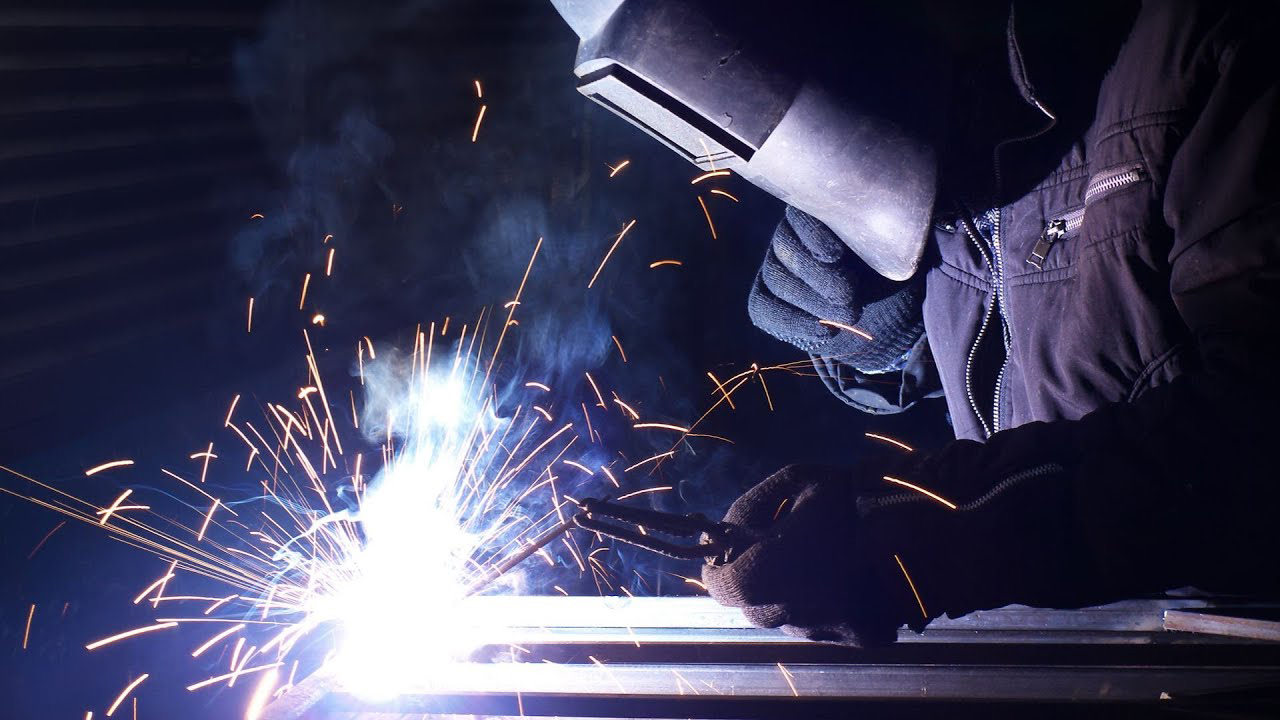
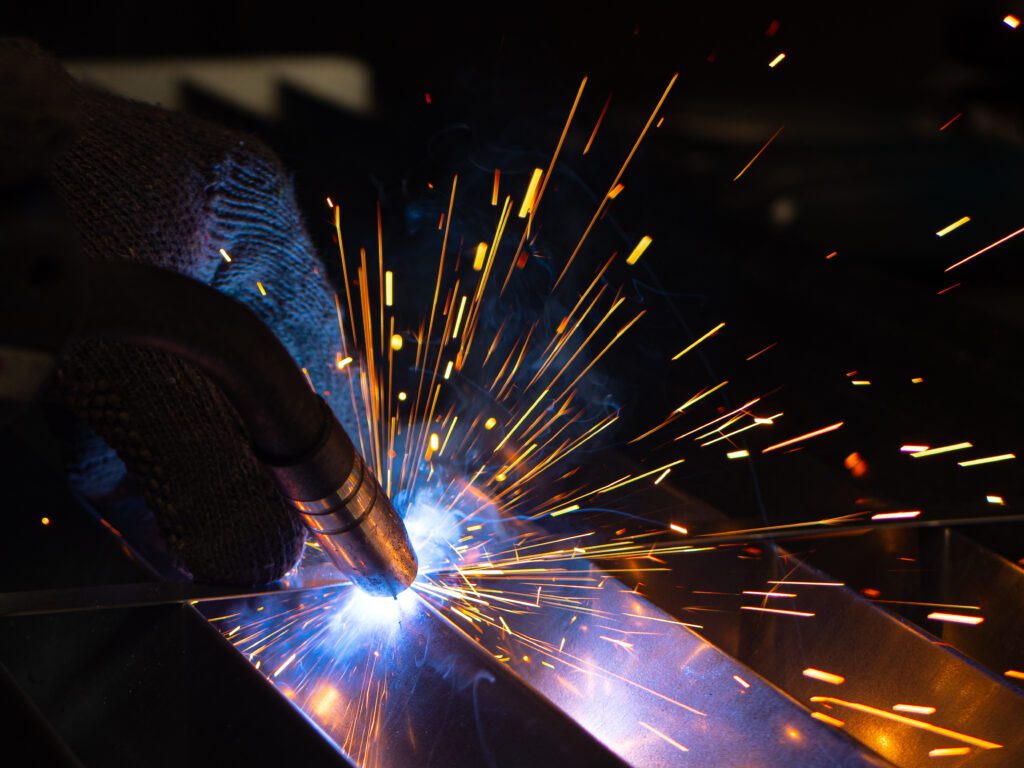
Welding: Fuses materials by melting them together, often with a filler material, creating strong permanent bonds
Brazing and Soldering: Joins metals by melting a metal alloy or a fusible filler and allowing it to flow into the space between the workpieces.
Riveting and Fastening: Mechanicallly fastens parts using rivets, screws, bolts and other mechanical fasteners.
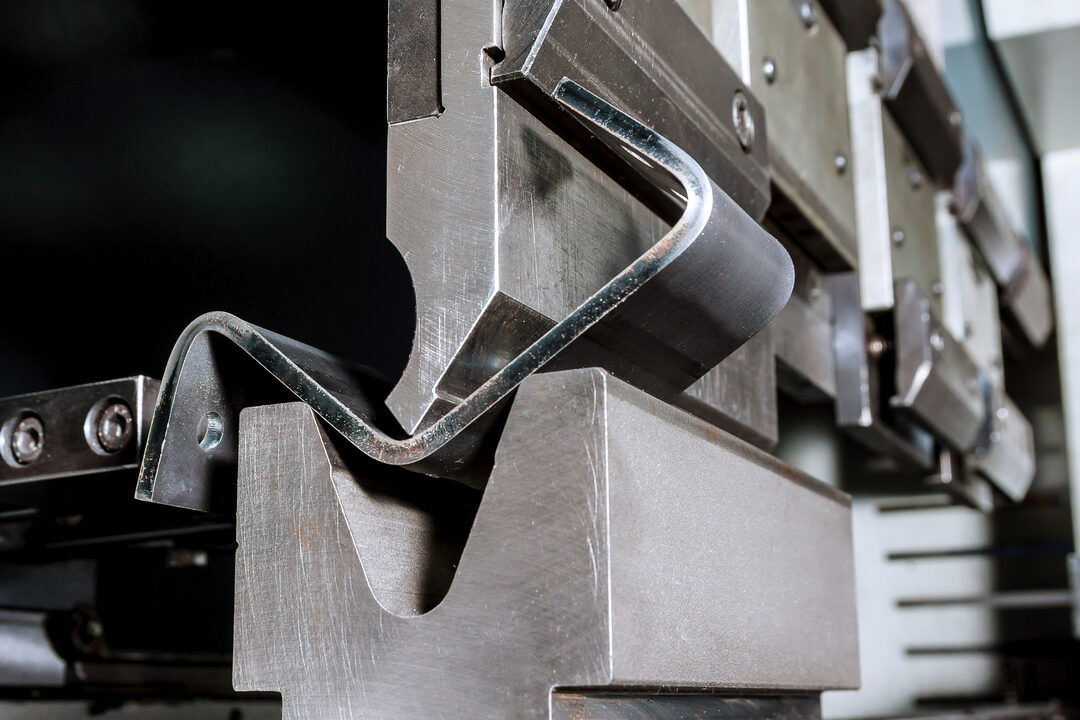
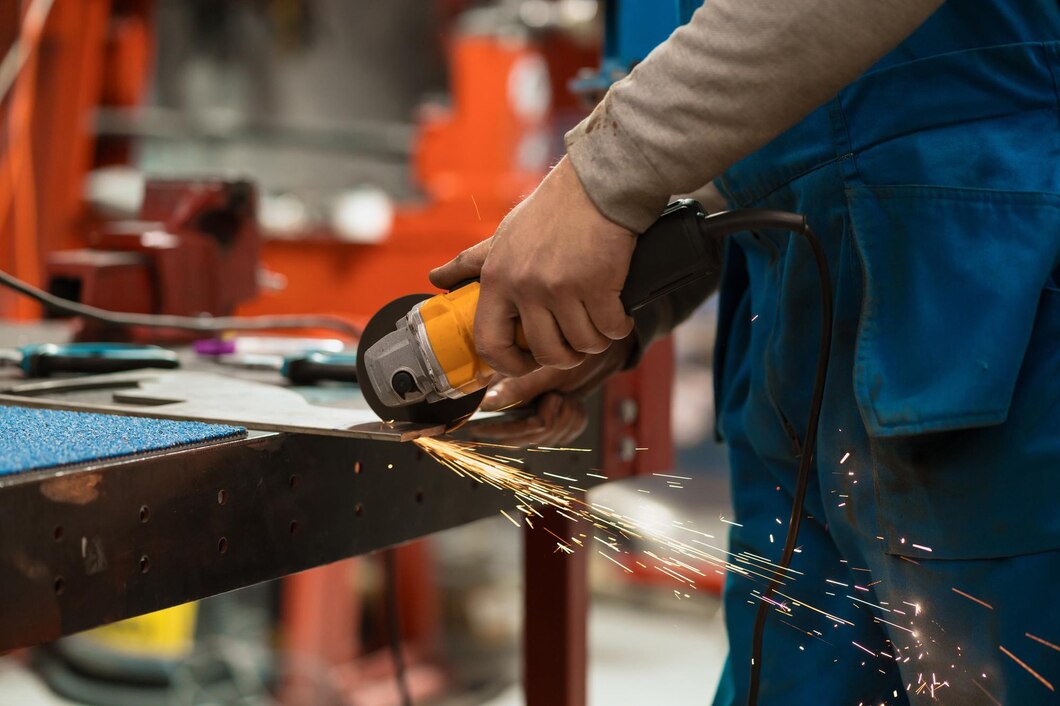
1. Sheet Metal Fabrication: Precision and Adaptability
Sheet metal fabrication is one of the most versatile and utilized fabrication processes in contemporary industry. This process specifically works with flat metal sheets, typically ranging from 0.15mm to 20mm in thickness, transforming them into parts and structures of various shapes.
The Sheet Metal Fabrication Method
.jpeg)
The process from flat metal sheet to final product is a usually typical process progression:
- Design and Engineering: Developing specifications and blueprints that drive fabrication.
- Material Selection: Selecting the correct material sheet metal based on requirements of the application, including strength, corrosion resistance, and formability.
- CUTTING: Making initial shapes by cutting with precision technologies like laser cutting, waterjet cutting , or plasma cutting from sheet metal.
- Forming: Applying shapes by bending, stamping or rolling the cut pieces into three-dimensional shapes.
- Assembling: Welding, Riveting, or the like, joining of a plurality of sheet metal elements.
- Finishing: The process of adding surface treatments, paint, powder coating, or simply finishes to improve the appear
The creation of sheet metal parts has come a long way with the use of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machinery that allows delicate contours with tight tolerances. This production process has been used to produce enclosures, cases, housing parts, metal frames, brackets, clips, stamped features, covers, lattices, perforated and blind vent holes, decorative trim, and lids of quality.
Uses for Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet Metal also possesses versatile properties, and this characteristic makes it indispensable in a vast array of industries like:
- Electronics: Forming enclosures, heat sinks and chassis
- The automotive sector: Manufacturing Body panels, brackets and structural parts
- HVAC: Manufacturing ductwork, vents and equipment enclosures
- Appliances: Fabricating frames, panels and housings for consumer goods
- Aerospace: Manufacturing of light weight structural elements and panels
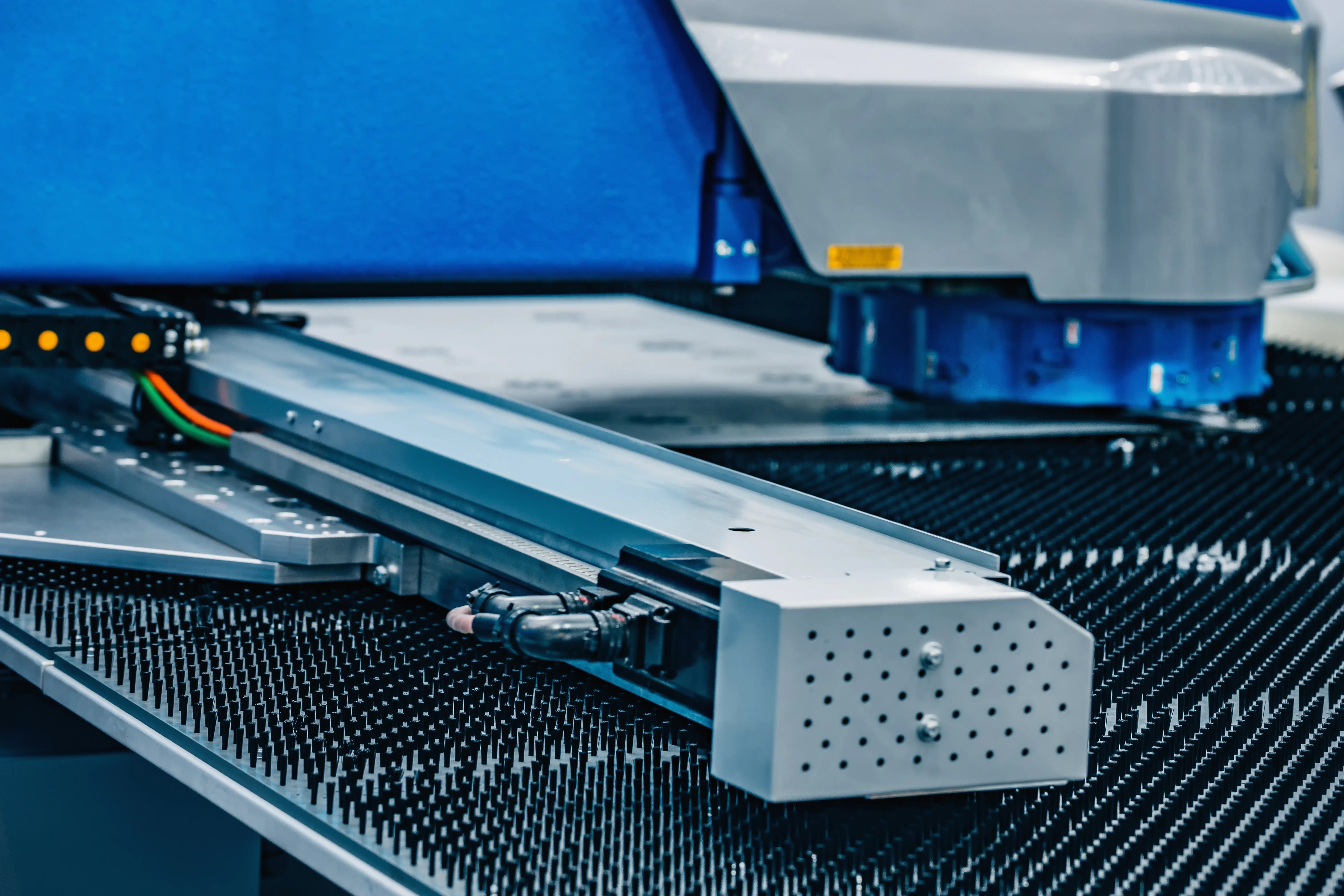
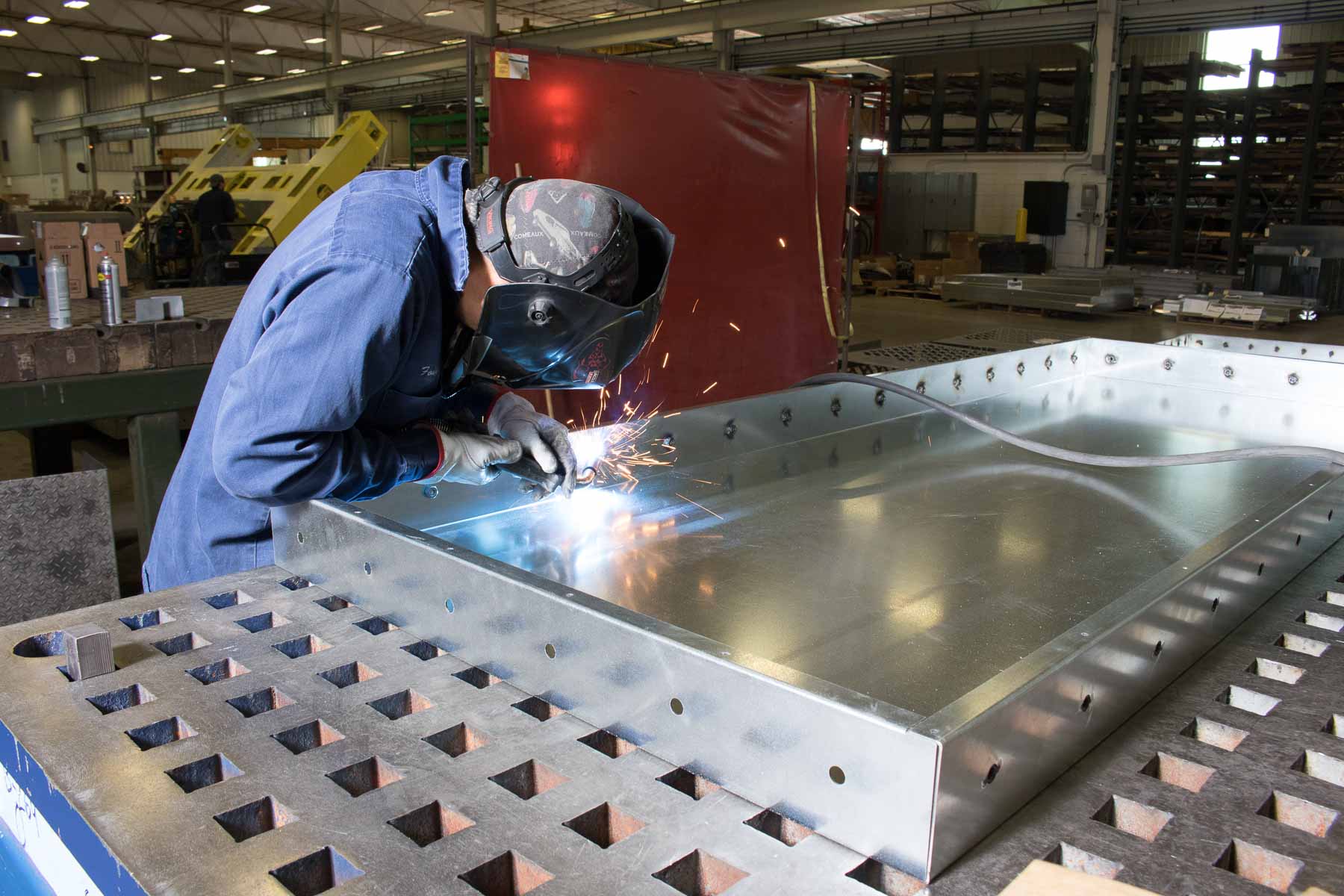
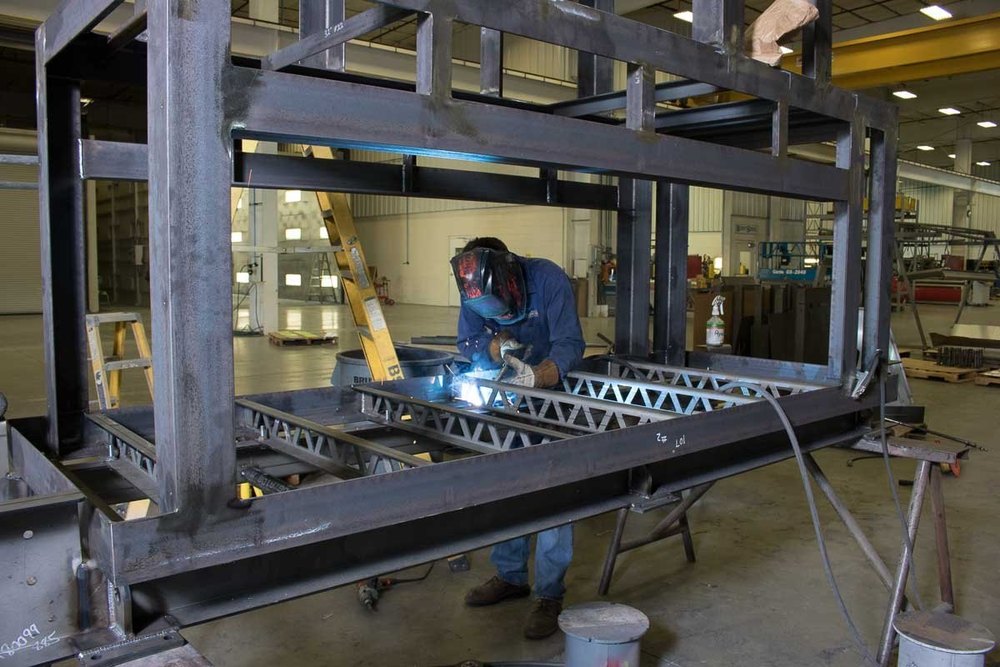
2. Structural Fabrication: Building the Framework
Structural fabrication is more specialized in the sense that it concerns the manufacture of metallic frameworks and members used to support loads and maintain the overall structure of buildings, bridges, and similar large-scale primary constructions.
The Process of Structural Fabrication
.jpg)
The stages of structural steel fabrication Structural steel fabrication is a multi-step process.
- Design Preparation: generating project drawings, specs and comprehensive BOMs that drive the manufacturing line.
- Material Acquisition: Purchasing standard or project specific length Material.
- Steel Cutting and Drilling: Cutting steel with the proper dimensions and required hole size on a CNC machine, circular saws, laser cutters, waterjets, or plasma machines.
- Bending and forming: The production of structural sections to size in accordance with the design.
- Welding & Assembly: Assembling system structures using engineering drawings.
- Surface Treatment: Surface protective painting is done to prevent the product from corrosion and to improve the product's durability.
- Quality Control: Checking all machined components prior to assembly for conformance to spec and quality.
Heavy gage steel is more commonly used in structural applications rather than plate based on the build to a structure as opposed to a code based on forming intricate structures. This action in turn establishes the framework relied on by buildings, bridges, and other large infrastructure.
3. Corrosion Resistant and Long Lasting: Stainless Steel Fabrication / SS Fabrication
In the same way, Stainless Steel Fabrication has its own unique set of skills required in order to fabricate with this corrosion resistant metal. Due to its particularities such as the chromium content and the corrosion resistance, stainless steel deserves the unique fabrication methods.
Stainless Steel Fabrication Process
Below are the main steps of the stainless steel fabrication process:
- Work Hardening: The compression or deformation of the metal through mechanical processes including hammering, rolling or pressing the increase the hardness and strength.
- Machining: Cutting and sculpting steel (which is harder to manipulate than other steel types due to its increased alloying content) with specialized tools and devices.
- Welding: Method to join stainless steel where the material retains its corrosion resistant proprieties due to special techniques employed in welding.
- Surface Treatment: To optimize appearance as well as functional purposes and to simultaneously assure corrosion resistance.
Uses of Stainless Steel Fabrication

Stainless Steel Fabrication is widely used where hygiene, corrosion resistance and high wear applications are essential:
- Food Processing Food Processing Equipment: Stainless steel vats, tanks, refrigeration units, countertops and other food processing equipment are all able to withstand the relentless assault of food acids and other compressors.
- Energy Industry: stainless steel fabrications such as oil and gas platforms, pipelines, components for renewable energy such as wind turbine bearings and emerging areas like wave power and tidal energy generation.
- Medical Devices: Surgical instruments, med tech parts, and healthcare facility fixtures.
- Chemical Processing: Tanks, pipes and vessels for transporting corrosive material.
4. Aluminum Fabrication: Lightweight Strength
Aluminum fabricators subsequently focus on working with this easily workable, rust-proof metal. The process is somewhat different from that used for steel because of aluminum’s special characteristics, which include a lower melting point and higher thermal conductivity.
Aluminium Fabrication Process
Although it is not made explicit in the search results provided and mentioned above, the fabrication of aluminum involves:
- Cutting: Using specialized tools optimized for aluminum's properties.
- Forming: Bending, rolling and shaping aluminum in ways that compliment its malleability.
- Assembly: The use of special welding processes such as TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas welding) or mechanical fastening solutions (for aluminium).
- Surface Treatment: Using anodizing, powder coating or other techniques to significantly increase material durability and improve appearance.
Uses of Aluminum Fabrication:
Aluminum fabrication is ideal for lightweight strength in the following common applications:
- Aerospace: Aircraft components, frames and paneling
- Automotive: Body panels, cherished parts and engine components
- Building: window and door frames and professional architectural systems
- Consumer Products: Enclosures for electronic devices, furniture, and decorative components
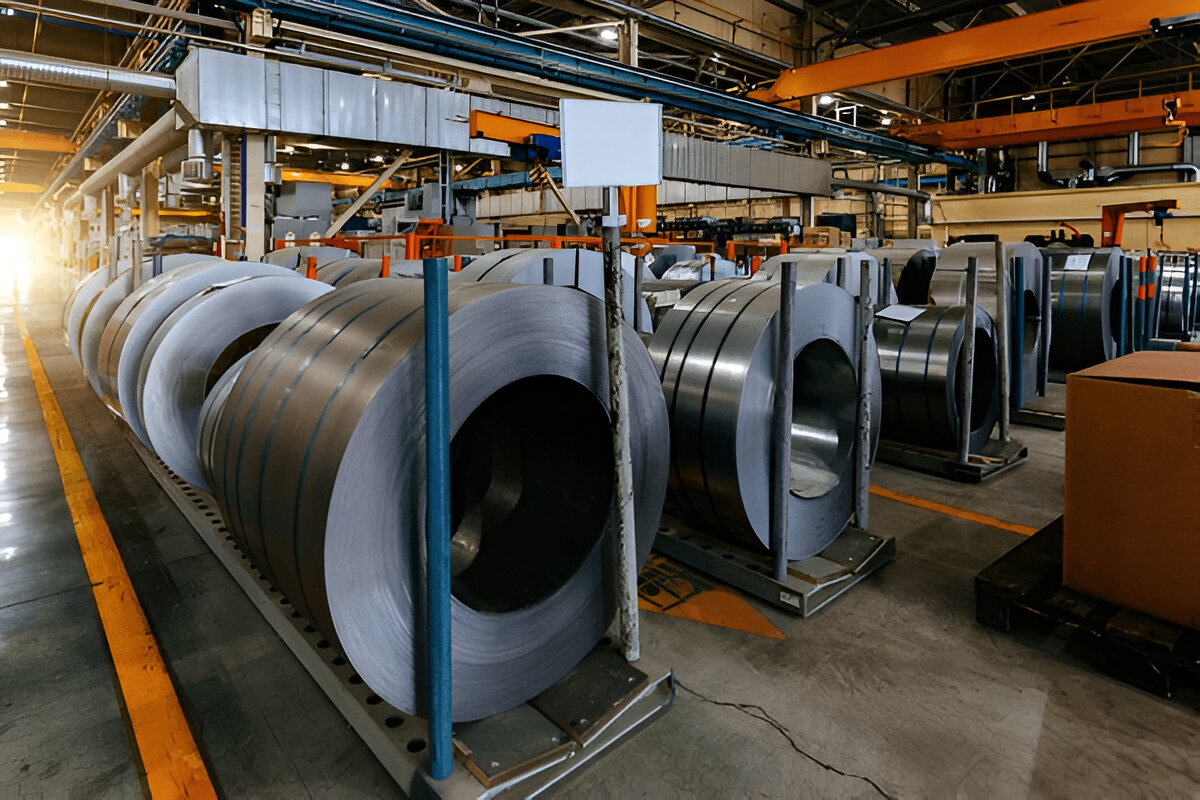
5. Industrial Fabrication: Scale Production
Industrial metal fabrication represents the large-scale application of fabrication techniques to create products and components for various industries. This holistic process employs a number of fabrication methods to produce the metal products society utilises on a daily basis.
Industrial Methods for Fabrication
Metal fabrication in a manufacturing setting is a complex method making use of a variety of methods to bend, cast, and mold the metal into the desired shape:
- Cutting: The technology will be used to cut large volumes of material in an efficient and accurate manner.
- Forming: Using presses, rolls, and other industrial scale equipment to form metal components.
- Joining: Combine adaptability (automatic welding and montage processes) with guarantee of constant quality at high rates.
- Finish: The form in which industrial surface treatments and coatings are applied by means of specialized equipment.
Industrial Fabrication Uses
.jpg)
Industrial fabrication serves as the backbone for a lot of industries:
- Construction: Building frames, structural components and architectural elements
- Manufacturing: Machinery Parts, workbenches, and tools of the trade
- Mechanical: Automotive parts, railway tracks and shipping vessels
- Energy: Power generation machinery, transmission towers, oil and gas equipment
Comparison of Different Fabrication Techniques
Each type of process has their own advantages according to the material you are using, the precision you need and what you want to do:
Material Considerations
- Sheet Metal Fabrication: Ideal use on thinner gauge metals for lightweight applications that require high quality welds.
- Structural Fabrication: Designed to handle heavy-duty applications in thicker steel.
- Stainless Steel Fabrication: Specialised for corrosion resistance and sanitary applications .
- Aluminium Fabrication: designed for light weight where the strength to weight ratio is critical.
Process Differences
- CUTTING Technology: is common to all the above and the technologies are different depending on the performed material and its thickness.
- Forming Methods: Sheet Metal Fabrication uses less press capacity and bending capacity tools compared to structural fabrication forming equipment.
- Joining Techniques: Stainless steel needs specialized welding methods to preserve its anti-corrosive properties, and aluminum needs methods adapted to its lower melting point.
Application Suitability
- Sheet Metal Fabrication: Great for enclosures, panels, brackets, and decorative parts.
- Structural Fabrication: Ideal for load bearing structures such as towers in bridges, buildings and large structures2.
- Stainless Steel Fabrication: Ideal for food processing, health care, commercial and industrial uses.
- Aluminum Fabricating: Ideal for light weight applications such as aerospace, automotive, and architectural.
Conclusion: What the Future Holds for Metal Fabrication
The metal fabrication industry is changing with the times, and technology has made precision and efficiency the name of the game. Fabrication is still being used today with old and new methods in the field of manufacturing and construction. Companies such as Zeometrix are leading the change by providing precision machining, sheet metal fabrication and all types of certified manufacturing processes to exacting industry specifications.
And as automation, advanced materials and digital technology become more and more embedded in fabrication processes, we should have the opportunity for even better precision, less waste and greater customisation potential. Zeometrix applies these technology advances, like Computer Numerically Controlled (CNC) machining, laser cutting, and digital quoting systems, to provide fast, top-quality solutions across a spectrum of industries.
Understanding the unique nature of different types of fabrication--be it sheet metal fabrication, structural fabrication, stainless steel fabrication, aluminum fabrication, or some other form of industrial fabrication--enables specialists to pick the best method for the job at hand. When working with partners like Zeometrix, companies are able to achieve optimal results in the areas of quality, function and cost.